add Data to a table
Add Data to a table
This tutorial explains several methods of entering data, from using a form, to SQL, to importing data from an external file.
But let's start off by entering data directly into a table in Datasheet View.
Add Records Directly into Datasheet View
This is probably the most obvious way to enter data into a database. Just open up the table and start typing.
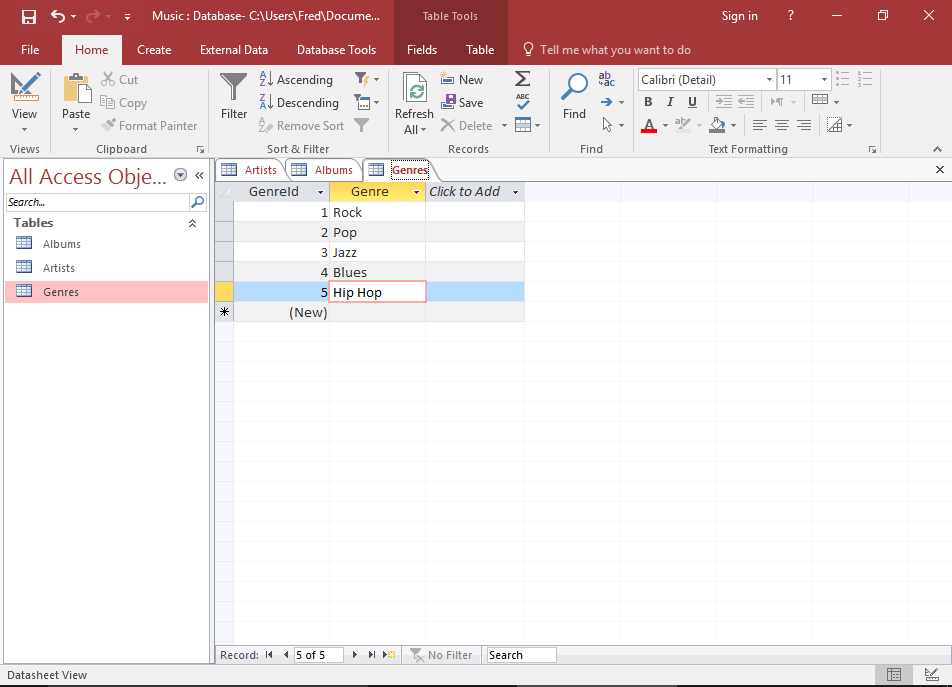
Open the Genres table in Datasheet View and enter the following data:
| GenreId* | Genre |
|---|---|
| (Autonumber) | Rock |
| (Autonumber) | Pop |
| (Autonumber) | Jazz |
| (Autonumber) | Blues |
| (Autonumber) | Hip Hop |
* No need to enter anything in the GenreId field. It's an Autonumber field, which means Access will populate it automatically
Pressing your keyboard's "down arrow" key will insert the record and move the cursor to the same field on the next record
Add Data using a Form
In many cases, you will want to create a form for users to enter data. This will allow them to enter data without needing any technical knowledge about Microsoft Access.
Forms can also improve usability and increase productivity. They can be used to update data across multiple tables, saving the user from having to open multiple tables and enter data into each one. They can also be use to provide extra data validation.
We'll be creating a form later in this tutorial.
Add Data using SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a query language designed specifically for relational databases. Most relational database management systems use SQL.
Most of the tasks that we've done so far in this tutorial, could easily have been done programatically, using SQL. In fact, behind the scenes, Access uses SQL to carry out the tasks that we specify through the user interface.
An example of an SQL statement to insert data looks like this:
INSERT INTO Genres (Genre)
VALUES ('Rock')
This tutorial doesn't go into the details of SQL, but if you're interested in learning more, check out the SQL tutorial.
This SQL tutorial consists of the following lessons


Comments
Post a Comment