Data fram in R programming
R - Data Frames
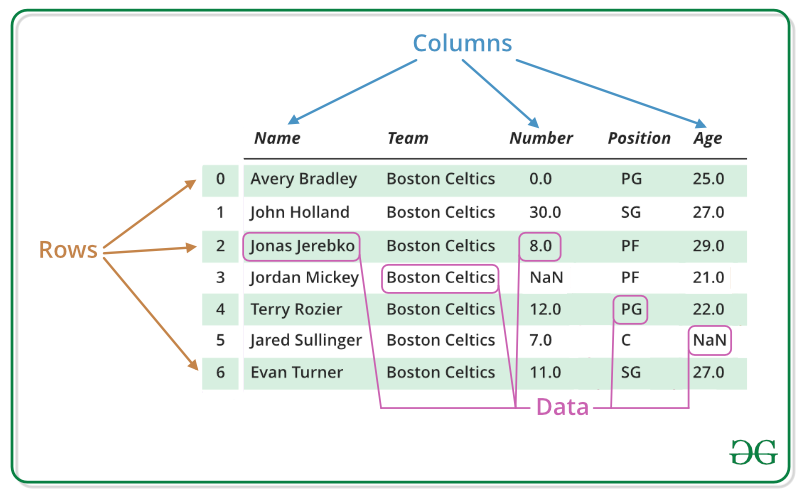
A data frame is a table or a two-dimensional array-like structure in which each column contains values of one variable and each row contains one set of values from each column.
Following are the characteristics of a data frame.
- The column names should be non-empty.
- The row names should be unique.
- The data stored in a data frame can be of numeric, factor or character type.
- Each column should contain same number of data items.
Create Data Frame
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Print the data frame. print(emp.data)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp_id emp_name salary start_date 1 1 Rick 623.30 2012-01-01 2 2 Dan 515.20 2013-09-23 3 3 Michelle 611.00 2014-11-15 4 4 Ryan 729.00 2014-05-11 5 5 Gary 843.25 2015-03-27
Get the Structure of the Data Frame
The structure of the data frame can be seen by using str() function.
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Get the structure of the data frame. str(emp.data)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
'data.frame': 5 obs. of 4 variables: $ emp_id : int 1 2 3 4 5 $ emp_name : chr "Rick" "Dan" "Michelle" "Ryan" ... $ salary : num 623 515 611 729 843 $ start_date: Date, format: "2012-01-01" "2013-09-23" "2014-11-15" "2014-05-11" ...
Summary of Data in Data Frame
The statistical summary and nature of the data can be obtained by applying summary() funct
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Print the summary. print(summary(emp.data))
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp_id emp_name salary start_date Min. :1 Length:5 Min. :515.2 Min. :2012-01-01 1st Qu.:2 Class :character 1st Qu.:611.0 1st Qu.:2013-09-23 Median :3 Mode :character Median :623.3 Median :2014-05-11 Mean :3 Mean :664.4 Mean :2014-01-14 3rd Qu.:4 3rd Qu.:729.0 3rd Qu.:2014-11-15 Max. :5 Max. :843.2 Max. :2015-03-27
Extract Data from Data Frame
Extract specific column from a data frame using column name.
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01","2013-09-23","2014-11-15","2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Extract Specific columns. result <- data.frame(emp.data$emp_name,emp.data$salary) print(result)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp.data.emp_name emp.data.salary 1 Rick 623.30 2 Dan 515.20 3 Michelle 611.00 4 Ryan 729.00 5 Gary 843.25
Extract the first two rows and then all columns
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Extract first two rows. result <- emp.data[1:2,] print(result)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp_id emp_name salary start_date 1 1 Rick 623.3 2012-01-01 2 2 Dan 515.2 2013-09-23
Extract 3rd and 5th row with 2nd and 4th column
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Extract 3rd and 5th row with 2nd and 4th column. result <- emp.data[c(3,5),c(2,4)] print(result)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp_name start_date 3 Michelle 2014-11-15 5 Gary 2015-03-27
Expand Data Frame
A data frame can be expanded by adding columns and rows.
Add Column
Just add the column vector using a new column name.
# Create the data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Add the "dept" coulmn. emp.data$dept <- c("IT","Operations","IT","HR","Finance") v <- emp.data print(v)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp_id emp_name salary start_date dept 1 1 Rick 623.30 2012-01-01 IT 2 2 Dan 515.20 2013-09-23 Operations 3 3 Michelle 611.00 2014-11-15 IT 4 4 Ryan 729.00 2014-05-11 HR 5 5 Gary 843.25 2015-03-27 Finance
Add Row
To add more rows permanently to an existing data frame, we need to bring in the new rows in the same structure as the existing data frame and use the rbind() function.
In the example below we create a data frame with new rows and merge it with the existing data frame to create the final data frame.
# Create the first data frame. emp.data <- data.frame( emp_id = c (1:5), emp_name = c("Rick","Dan","Michelle","Ryan","Gary"), salary = c(623.3,515.2,611.0,729.0,843.25), start_date = as.Date(c("2012-01-01", "2013-09-23", "2014-11-15", "2014-05-11", "2015-03-27")), dept = c("IT","Operations","IT","HR","Finance"), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Create the second data frame emp.newdata <- data.frame( emp_id = c (6:8), emp_name = c("Rasmi","Pranab","Tusar"), salary = c(578.0,722.5,632.8), start_date = as.Date(c("2013-05-21","2013-07-30","2014-06-17")), dept = c("IT","Operations","Fianance"), stringsAsFactors = FALSE ) # Bind the two data frames. emp.finaldata <- rbind(emp.data,emp.newdata) print(emp.finaldata)
When we execute the above code, it produces the following result −
emp_id emp_name salary start_date dept 1 1 Rick 623.30 2012-01-01 IT 2 2 Dan 515.20 2013-09-23 Operations 3 3 Michelle 611.00 2014-11-15 IT 4 4 Ryan 729.00 2014-05-11 HR 5 5 Gary 843.25 2015-03-27 Finance 6 6 Rasmi 578.00 2013-05-21 IT 7 7 Pranab 722.50 2013-07-30 Operations 8 8 Tusar 632.80 2014-06-17 Fianance
programming language that is widely used as a statistical software and data analysis tool. Data Frames in R Language are generic data objects of R which are used to store the tabular data. Data frames can also be interpreted as matrices where each column of a matrix can be of the different data types. DataFrame is made up of three principal components, the data, rows, and columns.
R – Data Frames
Create Dataframe in R Programming Language
create a data frame in R use data.() command and then pass each of the vectors you have created as arguments to the function.Example:R
# R program to create dataframe# creating a data framefriend.data <-data.frame(friend_id =c(1:5),friend_name =c("Sachin","Sourav","Dravid","Sehwag","Dhoni"),stringsAsFactors =FALSE)# print the data frame(friend.data)Output:
friend_id friend_name 1 1 Sachin 2 2 Sourav 3 3 Dravid 4 4 Sehwag 5 5 DhoniGet the Structure of the R – Data Frame
One can get the structure of the data frame using str() function in R. It can display even the internal structure of large lists which are nested. It provides one-liner output for the basic R objects letting the user know about the object and its constituents.
Example:
R
# R program to get the# structure of the data frame# creating a data framefriend.data <-data.frame(friend_id =c(1:5),friend_name =c("Sachin","Sourav","Dravid","Sehwag","Dhoni"),stringsAsFactors =FALSE)# using str()(str(friend.data))Output:
'data.frame': 5 obs. of 2 variables: $ friend_id : int 1 2 3 4 5 $ friend_name: chr "Sachin" "Sourav" "Dravid" "Sehwag" ... NULLSummary of data in the data frame
In R data frame, the statistical summary and nature of the data can be obtained by applying summary() function. It is a generic function used to produce result summaries of the results of various model fitting functions. The function invokes particular methods which depend on the class of the first argument.
Example:
R
# R program to get the# summary of the data frame# creating a data framefriend.data <-data.frame(friend_id =c(1:5),friend_name =c("Sachin","Sourav","Dravid","Sehwag","Dhoni"),stringsAsFactors =FALSE)# using summary()(summary(friend.data))Output:
friend_id friend_name Min. :1 Length:5 1st Qu.:2 Class :character Median :3 Mode :character Mean :3 3rd Qu.:4 Max. :5Extract Data from Data Frame in R Language
Extract data from a data frame means that to access its rows or columns. One can extract a specific column from a data frame using its column name.
Example:
R
# R program to extract# data from the data frame# creating a data framefriend.data <-data.frame(friend_id =c(1:5),friend_name =c("Sachin","Sourav","Dravid","Sehwag","Dhoni"),stringsAsFactors =FALSE)# Extracting friend_name columnresult <-data.frame(friend.data$friend_name)(result)Output:
friend.data.friend_name 1 Sachin 2 Sourav 3 Dravid 4 Sehwag 5 DhoniExpand Data Frame
A data frame in R can be expanded by adding new columns and rows to the already existing data frame.
Example:
R
# R program to expand# the data frame# creating a data framefriend.data <-data.frame(friend_id =c(1:5),friend_name =c("Sachin","Sourav","Dravid","Sehwag","Dhoni"),stringsAsFactors =FALSE)# Expanding data framefriend.data$location <-c("Kolkata","Delhi","Bangalore","Hyderabad","Chennai")resultant <- friend.data# print the modified data frame(resultant)Output:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni ChennaiIn R, one can perform various types of operations on a data frame like accessing rows and columns, selecting the subset of the data frame, editing data frames, delete rows and columns in a data frame, etc. Please refer to DataFrame Operations in R to know about all types of operations that can be performed on a data frame.



Comments
Post a Comment