The idea of banks began as long ago as 1,800 BC in Babylon. In those days moneylenders made loans to people. In Greece and Rome banks made loans and accepted deposits. They also changed money. (In the Bible Jesus famously drove the money changers out of the temple in Jerusalem).
However, with the collapse of the Roman Empire trade slumped and banks temporarily vanished. However, banking began to revive again in the 12th and 13th centuries in the Italian towns of Florence and Genoa.
In the 16th century, a German family called the Fuggers from Augsburg became very important bankers.
The Beginning of Banks in England
In England banks developed in the 17th century. Sometimes people deposited their money with goldsmiths for safety. The goldsmiths issued a note promising to pay the bearer a certain sum on demand. In time people began to exchange these notes instead of coins because it was easier and safer. Goldsmiths began to lend the money deposited with them in return for a high rate of interest. They also paid interest to people who deposited money in order to attract their savings.
However not only individuals borrowed money. Governments also needed to borrow, especially in wartime. The government borrowed money from wealthy individuals and later repaid them with interest from taxation.
However at the end of the 17th century the cost of fighting a war with France was colossal. So in 1694, the Bank of England was founded to provide
a loan to the government.
A group of financiers joined together to provide the money required to set up the bank and loan the government 1.2 million pounds (a massive sum in those days). In return, the bank received an 8% interest on the loan and the right to issue notes. The Bank of England was also allowed to lend money and to buy and sell gold.
The Bank of England is sometimes called the ‘Old Lady of Threadneedle Street’. In fact, it moved to Threadneedle Street in 1734. Meanwhile, the Bank of Scotland was founded in 1695.
In 1708 a law forbade banks with more than 6 partners to issue their own notes. (Although small banks could still do so). However, the Bank of England mostly confined its operations to London. In the late 18th century many small banks were founded in the provincial towns. the first traveler’s cheques were issued in England in 1772.
However, banking crises are nothing new. In 1793, in 1814-1816, and in 1825 there were ‘runs’ on banks when people lost confidence and tried to withdraw their money. The result each time was a wave of bank failures.
In 1826 the law was changed to allow large banks with many shareholders to form outside London. Many of the small country banks merged with the large banks.
In 1833 banknotes issued by the Bank of England were made legal tender (they must be accepted as payment for a debt).
The first commercial bank in the USA was the Bank of North America, which opened in 1782.
Modern Banks
In Britain, modern banks began with the Bank Charter Act of 1844. The Act split the Bank of England (which was still legally a private bank) into two departments – a banking department and an issuing department. From then on the Bank of England could only issue notes if they were backed up by gold or government securities.
The Bank Charter Act also forbade new banks to issue banknotes. When banks merged they lost the right to issue banknotes. So gradually the Bank of England became the only bank in England that could issue notes.
At the end of the 19th century and in the 20th century many banks merged until in the late 20th-century banking in Britain was dominated by the ‘big four’, Barclays, Lloyds, Midland, and National Westminster.
The Bank of England n In 1946 the Bank of England was finally nationalized. Also in 1946, the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (otherwise known as the World Bank) was formed.
In 1967 Barclays Bank installed the first cash dispensing machine in Britain at a branch in Enfield, London. Internet banking began in Britain in 199
History
Ancient India
The Vedas are the ancient Indian texts mention the concept of usury, with the word kusidin translated as "usurer". The Sutras (700–100 BCE) and the Jatakas (600–400 BCE) also mention usury. Texts of this period also condemned usury: Vasishtha forbade Brahmin and Kshatriya varnas from participating in usury. By the 2nd century CE, usury became more acceptable.[11] The Manusmriti considered usury an acceptable means of acquiring wealth or leading a livelihood.[12] It also considered money lending above a certain rate and different ceiling rates for different castes a grave sin.[13]
The Jatakas, Dharmashastras and Kautilya also mention the existence of loan deeds, called rnapatra, rnapanna, or rnalekhaya.[14][15]
Later during the Mauryan period (321–185 BCE), an instrument called adesha was in use, which was an order on a banker directing him to pay the sum on the note to a third person, which corresponds to the definition of a modern bill of exchange. The considerable use of these instruments has been recorded[citation needed]. In large towns, merchants also gave letters of credit to one another.
Medieval Period
The use of loan deeds continued into the Mughal era and were called dastawez (in Urdu/Hindi). Two types of loans deeds have been recorded. The dastawez-e-indultalab was payable on demand and dastawez-e-miadi was payable after a stipulated time. The use of payment directives by royal treasuries, called barattes, have been also recorded. There are also records of Indian bankers using issuing bills of exchange on foreign countries. The evolution of hundis, a type of credit instrument, also occurred during this period and remain in use.Colonial era
During the period of British rule merchants established the Union Bank of Calcutta in 1829, first as a private joint stock association, then partnership. Its proprietors were the owners of the earlier Commercial Bank and the Calcutta Bank, who by mutual consent created Union Bank to replace these two banks. In 1840 it established an agency at Singapore, and closed the one at Mirzapore that it had opened in the previous year. Also in 1840 the Bank revealed that it had been the subject of a fraud by the bank's accountant. Union Bank was incorporated in 1845 but failed in 1848, having been insolvent for some time and having used new money from depositors to pay its dividends.
The Allahabad Bank, established in 1865 and still functioning today, is the oldest Joint Stock bank in India, it was not the first though. That honour belongs to the Bank of Upper India, which was established in 1863 and survived until 1913, when it failed, with some of its assets and liabilities being transferred to the Alliance Bank of Simla.
Foreign banks too started to appear, particularly in Calcutta, in the 1860s. Grindlays Bank opened its first branch in Calcutta in 1864.[18] The Comptoir d'Escompte de Paris opened a branch in Calcutta in 1860, and another in Bombay in 1862; branches followed in Madras and Pondicherry, then a French possession. HSBC established itself in Bengal in 1869. Calcutta was the most active trading port in India, mainly due to the trade of the British Empire, and so became a banking centre.
The first entirely Indian joint stock bank was the Oudh Commercial Bank, established in 1881 in Faizabad. It failed in 1958. The next was the Punjab National Bank, established in Lahore in 1894, which has survived to the present and is now one of the largest banks in India.
Around the turn of the 20th century, the Indian economy was passing through a relative period of stability. Around five decades had elapsed since the Indian rebellion, and the social, industrial and other infrastructure had improved. Indians had established small banks, most of which served particular ethnic and religious communities.
The presidency banks dominated banking in India but there were also some exchange banks and a number of Indian joint stock banks. All these banks operated in different segments of the economy. The exchange banks, mostly owned by Europeans, concentrated on financing foreign trade. Indian joint stock banks were generally under capitalised and lacked the experience and maturity to compete with the presidency and exchange banks. This segmentation let Lord Curzon to observe, "In respect of banking it seems we are behind the times. We are like some old fashioned sailing ship, divided by solid wooden bulkheads into separate and cumbersome compartments.
The period between 1906 and 1911 saw the establishment of banks inspired by the Swadeshi movement. The Swadeshi movement inspired local businessmen and political figures to found banks of and for the Indian community. A number of banks established then have survived to the present such as Catholic Syrian Bank, The South Indian Bank, Bank of India, Corporation Bank, Indian Bank, Bank of Baroda, Canara Bank and Central Bank of India.
The fervour of Swadeshi movement led to the establishment of many private banks in Dakshina Kannada and Udupi district, which were unified earlier and known by the name South Canara (South Kanara) district. Four nationalised banks started in this district and also a leading private sector bank. Hence undivided Dakshina Kannada district is known as "Cradle of Indian Banking".[citation needed]
The inaugural officeholder was the Britisher Sir Osborne Smith(1 April 1935), while C. D. Deshmukh(11 August 1943) was the first Indian governor. On 12 December 2018,Shaktikanta Das, who was the finance secretary with the Government of India, begins his journey as the new RBI Governor, taking charge from Urjit R Patel.
During the First World War (1914–1918) through the end of the Second World War (1939–1945), and two years thereafter until the independence of India were challenging for Indian banking. The years of the First World War were turbulent, and it took its toll with banks simply collapsing despite the Indian economy gaining indirect boost due to war-related economic activities. At least 94 banks in India failed between 1913 and 1918 as indicated in the following table:
| Years | Number of banks that failed | Authorised Capital (₹ Lakhs) | Paid-up Capital (₹ Lakhs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1913 | 12 | 274 | 35 |
| 1914 | 42 | 710 | 109 |
| 1915 | 11 | 56 | 5 |
| 1916 | 13 | 231 | 4 |
| 1917 | 9 | 76 | 25 |
| 1918 | 7 | 209 | 1 |
Post-Independence
During 1938–46, bank branch offices trebled to 3,469 and deposits quadrupled to ₹ 962 crore. Nevertheless, the partition of India in 1947 adversely impacted the economies of Punjab and West Bengal, paralysing banking activities for months. India's independence marked the end of a regime of the Laissez-faire for the Indian banking. The Government of India initiated measures to play an active role in the economic life of the nation, and the Industrial Policy Resolution adopted by the government in 1948 envisaged a mixed economy. This resulted in greater involvement of the state in different segments of the economy including banking and finance. The major steps to regulate banking included:
The Reserve Bank of India, India's central banking authority, was established in April 1935, but was nationalized on 1 January 1949 under the terms of the Reserve Bank of India (Transfer to Public Ownership) Act, 1948 (RBI, 2005b).
In 1949, the Banking Regulation Act was enacted, which empowered the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to regulate, control, and inspect the banks in India.
The Banking Regulation Act also provided that no new bank or branch of an existing bank could be opened without a license from the RBI, and no two banks could have common directors.
Nationalisation in 1969
- Allahabad Bank (now Indian Bank)
- Bank of Baroda
- Bank of India
- Bank of Maharashtra
- Central Bank of India
- Canara Bank
- Dena Bank (now Bank of Baroda)
- Indian Bank
- Indian Overseas Bank
- Punjab National Bank
- Syndicate Bank (now Canara Bank)
- UCO Bank
- Union Bank of India
- United Bank of India( now Punjab National Bank)
Nationalisation in 1980
A second round of nationalizations of six more commercial banks followed in 1980. The stated reason for the nationalization was to give the government more control of credit delivery. With the second round of nationalizations, the Government of India controlled around 91% of the banking business of India.
The following banks were nationalized in 1980:
- Punjab and Sind Bank
- Vijaya Bank (Now Bank of Baroda)
- Oriental Bank of Commerce (now Punjab National Bank)
- Corporation Bank (now Union Bank of India)
- Andhra Bank (now Union Bank of India)
- New Bank of India (now Punjab National Bank)
Later on, in the year 1993, the government merged New Bank of India with Punjab National Bank. It was, at that time, the only merger between nationalised banks and resulted in the reduction of their number from 20 to 19. Until the 1990s, the nationalized banks grew at a pace of around 4%, closer to the average growth rate of the Indian economy.
Liberalisation in the 1990s
In the early 1990s, the then government embarked on a policy of liberalisation licensing a small number of private banks.These came to be known as New Generation tech-savvy banks, and included Global Trust Bank (the first of such new generation banks to be set up), which later amalgamated with Oriental Bank of Commerce, IndusInd Bank, UTI Bank (since renamed Axis Bank), ICICI Bank and HDFC Bank.[28] This move – along with the rapid growth in the economy of India – revitalised the banking sector in India, which has seen rapid growth with strong contribution from all the three sectors of banks, namely, government banks, private banks and foreign banks.
The next stage for the Indian banking has been set up, with proposed relaxation of norms for foreign direct investment. All foreign investors in banks may be given voting rights that could exceed the present cap of 10% at present. In 2019, Bandhan bank specifically, increased the foreign investment percentage limit to 49%. It has gone up to 74% with some restrictions.
The new policy shook the banking sector in India completely. Bankers, till this time, were used to the 4–6–4 method (borrow at 4%; lend at 6%; go home at 4) of functioning. The new wave ushered in a modern outlook and tech-savvy methods of working for traditional banks. All this led to the retail boom in India. People demanded more from their banks and received more.
PSB Amalgamations in the 2000s and 2010s
SBI
SBI merged with its associate bank State Bank of Saurashtra in 2008 and State Bank of Indore in 2009.
Following a merger process, the merger of the 5 remaining associate banks, (viz. State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur, State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of Mysore, State Bank of Patiala, State Bank of Travancore); and the Bharatiya Mahila Bank) with the SBI was given an in-principle approval by the Union Cabinet on 15 June 2016. This came a month after the SBI board had, on 17 May 2016, cleared a proposal to merge its five associate banks and Bharatiya Mahila Bank with itself.
On 15 February 2017, the Union Cabinet approved the merger of five associate banks with SBI. An analyst foresaw an initial negative impact as a result of different pension liability provisions and accounting policies for bad loans.The merger went into effect from 1 April 2017.
BOB
On 17 September 2018, the Government of India proposed the amalgamation of Dena Bank and Vijaya Bank with erstwhile Bank of Baroda, pending (namesake) approval from the boards of the three banks.[40] The Union Cabinet and the boards of the banks approved with the merger on 2 January 2019. Under the terms of the amalgamation, Dena Bank and Vijaya Bank shareholders received 110 and 402 equity shares of the Bank of Baroda, respectively, of face value ₹2 for every 1,000 shares they held. The amalgamation became effective from 1 April 2019.
PNB
On 30 August 2019, Finance Minister announced that the Oriental Bank of Commerce and United Bank of India would be merged with Punjab National Bank, making PNB the second largest PSB after SBI with assets of ₹17.95 lakh crore (US$220 billion) and 11,437 branches. MD and CEO of UBI, Ashok Kumar Pradhan, stated that the merged entity would begin functioning from 1 April 2020. The Union Cabinet approved the merger on 4 March 2020. PNB announced that its board had approved the merger ratios the next day. Shareholders of OBC and UBI will receive 1,150 shares and 121 shares of Punjab National Bank, respectively, for every 1,000 shares they hold. The merge came into effect since 1 April 2020. Post merger, Punjab National Bank has become the second largest public sector bank in India
Canara Bank
On 30 August 2019, Finance Minister announced that Syndicate Bank would be merged with Canara Bank. The proposal would create the fourth largest PSB trailing SBI, PNB, BoB with assets of ₹15.20 lakh crore (US$190 billion) and 10,324 branches.The Board of Directors of Canara Bank approved the merger on 13 September 2019.The Union Cabinet approved the merger on 4 March 2020. Canara Bank assumed control over Syndicate Bank on 1 April 2020 with Syndicate Bank shareholders receiving 158 equity shares in the former for every 1,000 shares they hold.
Union Bank of India
On 30 August 2019, Finance Minister announced that Andhra Bank and Corporation Bank would be merged into Union Bank of India. The proposal would make Union Bank of India the fifth largest PSB with assets of ₹14.59 lakh crore (US$180 billion) and 9,609 branches. The Board of Directors of Andhra Bank approved the merger on 13 September. The Union Cabinet approved the merger on 4 March, and it was completed on 1 April 2020
Indian Bank
On 30 August 2019, Finance Minister announced that Allahabad Bank would be merged with Indian Bank. The proposal would create the seventh largest PSB in the country with assets of ₹8.08 lakh crore (US$100 billion).The Union Cabinet approved the merger on 4 March 2020. Indian Bank assumed control of Allahabad Bank on 1 April 2020.
Rescue of private and co-operative banks (2020s)
Yes bank
In April 2020, RBI enlisted SBI to rescue the troubled lender Yes Bank, in the form of investment with assistance from other lenders viz., ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank and Kotak Mahindra Bank. SBI went on to own 48% share capital of Yes bank, which it later diluted to 30% in an FPO in the following months.
Lakshmi Vilas Bank
In November 2020, RBI asked DBS Bank India Limited (DBIL) to take over the operations of the private sector bank Lakshmi Vilas Bank whose net worth has turned negative, following mismanagement and two failed merger attempts with NBFCs. DBS India's then having just 12 branches benefited by LVB's 559 branches. In a first of a kind move, Tier- II bond holders have been asked by RBI to write off their holdings in LVB.
Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative Bank
In January 2022, RBI asked Unity Small Finance Bank Limited (Unity SFB) to take over the operations of the private sector bank Punjab and Maharashtra Co-operative Bank (PMC), following mismanagement and one failed merger attempts with NBFC/SFBs. Unity SFB then was being created by Centrum Finance and payment provider BharatPe to absorb the liabilities of the scam hit bank. In a first of a kind move, RBI allowed an established cooperative bank to merge into a then being created SFB.
Regional Rural banks revamp
With a new policy effected in late 2010, the RRBs which served a smaller locality spanning a few districts, were merged into a state level entity following the merger of nationalised banks and their equity in RRBs getting sequentially higher. This eliminated the existential competition and cooperation between RRB's and essentially making them a subsidiary bank of the promoter nationalised bank with state equity.
Current period
The Indian banking sector is broadly classified into scheduled banks and non-scheduled banks. All banks included in the Second Schedule to the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 are Scheduled Banks. These banks comprise Scheduled Commercial Banks and Scheduled Co-operative Banks. Scheduled Co-operative Banks consist of Scheduled State Co-operative Banks and Scheduled Urban Cooperative Banks.
In the bank group-wise classification, IDBI Bank Ltd. is included in the category of other public sector bank.
| Indicators | 31 March of | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| Number of Commercial Banks | 284 | 218 | 178 | 169 | 166 | 163 | 163 | 169 | 151 |
| Number of Branches | 70,373 | 72,072 | 74,653 | 78,787 | 82,897 | 88,203 | 94,019 | 102,377 | 109,811 |
| Population per Banks (in thousands) | 16 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 12 |
| Aggregate Deposits | ₹17,002 billion (US$210 billion) | ₹21,090 billion (US$260 billion) | ₹26,119 billion (US$330 billion) | ₹31,969 billion (US$400 billion) | ₹38,341 billion (US$480 billion) | ₹44,928 billion (US$560 billion) | ₹52,078 billion (US$650 billion) | ₹59,091 billion (US$740 billion) | ₹67,504.54 billion (US$850 billion) |
| Bank Credit | ₹11,004 billion (US$140 billion) | ₹15,071 billion (US$190 billion) | ₹19,312 billion (US$240 billion) | ₹23,619 billion (US$300 billion) | ₹27,755 billion (US$350 billion) | ₹32,448 billion (US$410 billion) | ₹39,421 billion (US$490 billion) | ₹46,119 billion (US$580 billion) | ₹52,605 billion (US$660 billion) |
| Deposit as percentage to GNP (at factor cost) | 62% | 64% | 69% | 73% | 77% | 78% | 78% | 78% | 79% |
| Per Capita Deposit | ₹16,281 (US$200) | ₹19,130 (US$240) | ₹23,382 (US$290) | ₹28,610 (US$360) | ₹33,919 (US$420) | ₹39,107 (US$490) | ₹45,505 (US$570) | ₹50,183 (US$630) | ₹56,380 (US$710) |
| Per Capita Credit | ₹10,752 (US$130) | ₹13,869 (US$170) | ₹17,541 (US$220) | ₹21,218 (US$270) | ₹24,617 (US$310) | ₹28,431 (US$360) | ₹34,187 (US$430) | ₹38,874 (US$490) | ₹44,028 (US$550) |
| Credit Deposit Ratio | 63% | 70% | 74% | 75% | 74% | 74% | 76% | 79% | 79% |
With the growth in the Indian economy expected to be strong for quite some time-especially in its services sector-the demand for banking services, especially retail banking, mortgages and investment services are expected to be strong. One may also expect M&As, takeovers, and asset sales.
In March 2006, the Reserve Bank of India allowed Warburg Pincus to increase its stake in Kotak Mahindra Bank (a private sector bank) to 10%. This was the first time an investor was allowed to hold more than 5% in a private sector bank since the RBI announced norms in 2005 that any stake exceeding 5% in the private sector banks would need to be vetted by them.
In recent years critics have charged that the non-government owned banks are too aggressive in their loan recovery efforts in connection with housing, vehicle and personal loans. There are press reports that the banks' loan recovery efforts have driven defaulting borrowers to suicide.
By 2013 the Indian Banking Industry employed 1,175,149 employees and had a total of 109,811 branches in India and 171 branches abroad and manages an aggregate deposit of ₹67,504.54 billion (US$850 billion or €830 billion) and bank credit of ₹52,604.59 billion (US$660 billion or €640 billion). The net profit of the banks operating in India was ₹1,027.51 billion (US$13 billion or €13 billion) against a turnover of ₹9,148.59 billion (US$110 billion or €110 billion) for the financial year 2012–13.
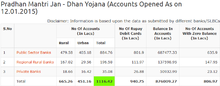
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (Hindi: प्रधानमंत्री जन धन योजना, English: Prime Minister's People Money Scheme) is a scheme for comprehensive financial inclusion launched by the Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, in 2014.Run by Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, on the inauguration day, 1.5 Crore (15 million) bank accounts were opened under this scheme. By 15 July 2015, 16.92 crore accounts were opened, with around ₹20,288.37 crore (US$2.5 billion) were deposited under the scheme, which also has an option for opening new bank accounts with zero balance.
Payment Bank
Payments bank is a new model of banks conceptualized by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). These banks can accept a restricted deposit, which is currently limited to ₹2 lakh per customer. These banks may not issue loans or credit cards, but may offer both current and savings accounts. Payments banks may issue ATM and debit cards, and offer net-banking and mobile-banking. The draft guidelines for licensing of payments banks in the private sector were formulated and released for public comments on 17 July 2014. The banks will be licensed as payments banks under Section 22 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, and will be registered as public limited company under the Companies Act, 2013.
Small finance banks
To further the objective of financial inclusion, the RBI granted approval in 2016 to ten entities to set up small finance banks. Since then, all ten have received the necessary licenses. A small finance bank is a niche type of bank to cater to the needs of people who traditionally have not used scheduled banks. Each of these banks is to open at least 25% of its branches in areas that do not have any other bank branches (unbanked regions). A small finance bank should hold 75% of its net credits in loans to firms in priority sector lending, and 50% of the loans in its portfolio must be less than ₹25 lakh (US$34,000).
Banking codes and
The Banking Codes and standards Board of India is an independent and autonomous banking industry body that monitors banks in India.To improve the quality of banking services in India S S Tarapore (former deputy governor of RBI) had the idea to form this committee



Comments
Post a Comment